|
|
||
SENUBIO group > Medical-physics engineering
Line 1. Quality control, evaluation and improvement for radiological treatments and equipments
The objective of this line is to reduce the given doses by ionizing radiation in medical treatments (nuclear medicine, radiodiagnosis, radiotherapy, braquitherapy, etc).
For this, depending on the medical treatment or equipment to be studied, we are using different techniques, being the Monte Carlo method mainly used for the dose calculation during the treatment.
Nowadays, the group is working mainly in the following projects:
- Quality control for X-ray facilities.. This project consist on the development of a new tool for quality control to be applied in different radiological systems (conventional radiology equipment, analogic and digital mammography, computerized tomography (CT), industrial x-ray equipment, etc.), based in the use of specific phantoms that allow the obtention of an image to be evaluated. In this way, the quality of the obtained images gives us a measure of its obtention methodology quality.
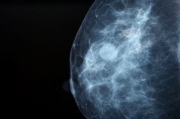
- Digital mammography equipment validation.. The objective is the development of new validation techniques for the correct mammographyc digital equipment performance. The image quality is evaluated and also the medium dose absorbed in each exposition. New quality indicators are to be defined or revised, from an image quality optimization point of view and the dose minimization. For the dose estimation we are developing new reconstruction methodologies (with Monte Carlo methods), calculating in these simulations the deposited energy.
- Quality control for X-ray facilities with the spectrum reconstruction.. In this project, an x-ray equipment validation methodology will be developed. The methodology consist on the comparison between its specifications and the reconstructed spectrum with deconvolution techniques.
Line 2. Radiotherapy Planning System development
Dose distribution calculation by means of a new methodology based in Monte Carlo method. In this way, and from a tridimensional image generated from CT of an atropomorphyc phantom, it will be developed a model for the organs to be irradiated and so for the around organs. Also the irradiation source and field will be simulated.
Line 3. Radiographic images evaluation
Some medical diagnosis techniques distribute great doses to the patients, so fast diagnosis would considerably reduce the distributed doses. In addition, in the case of tumours diagnosis, any information of the tumour location is necessary to be able to give effective therapies.
In this way, we are studying techniques to improve different elements detection that are difficult to distinguish due to its small size and the noisy images conditions. It is being studied the development and application of mathematical processing techniques, such as wavelets, diffusion equations, independent components analysis, morphologic operators, etc., for the detection of tumour like injuries in medical images, such as microcalcifications in mammography. Hence, it is possible to eliminate noise and to improve the diagnosis by means of automatic detection. We expect to provide one second reading that allows the radiologist to assure diagnose.
Also the application of the Monte Carlo method in the reconstruction of radiodiagnosis images is being studied, mainly in digital and conventional mammography, where the low energies along with the variations of density between weaves make difficult any method of reconstruction.
Some specific results obtained through this research line are:
- RADEN Software: software for the quality control of dental radiodiagnosis equipment by means of phantoms image evaluation.
- RACON Software: software for the quality control of radiography and radioscopy equipment by means of phantoms image evaluation.
Line 4. Radiological detriment calculation
The objective of this research line is the calculation of the risk or radiological damage on the basis of the doses considered in analogical or digital mammography.
The obtained results are being applied at the moment to the Breast Cancer Screening Programme of the Valencian Community.
Line 5. Radiological protection
In this line dose calculation by means of Monte Carlo methods will be performed, in order to estimate isodose maps and Germanium detectors calibrations.
Results are being applied at the moment to the dose calculation in nuclear power plants.
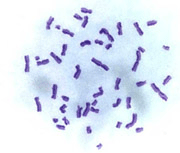
Line 6. Biological dosimetry
Biological Dosimetry is a technique that allows the estimative determination of the exposition degree to ionizing radiations through the evaluation of the caused biological effects. At the moment, group SENUBIO works in the following fields:
- Citogenetic analysis of peripheral blood lymphocytes;
- Chromosomic aberrations study in exposed individuals to chemical agents;
- Evaluation of the radioprotector effect of certain substances;
The irradiation accidents imply to all population categories, public and workers. The biological dosimetry aid to define the state of the patient, as complement of the physical dosimetry (dosimeter) and the medical examination.
This is particularly useful for those people susceptible to be radiated and not to wear the dosimeter at the moment of the exposition. Its main role is to verify if the exposition has taken place. Later, if the exposition is verified, the given dose is estimated. The analysis of unstable type chromosomic alterations (dicentrics and rings) is considered the more specific and sensible biological dosimetry method.
|